If you’ve ever wondered what is DNS, you’re not alone. DNS is one of the most important parts of how the internet works, yet most people never notice it running quietly in the background. Every time you open a website, send an email, or connect to an online service, DNS helps your device find the right destination.
In simple terms, DNS makes the internet easier for humans to use by translating domain names into machine-readable IP addresses.
For example, when you type webhostingpeople.com into your browser, DNS helps your computer locate the exact server where that website is hosted.
Understanding DNS in Simple Words
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It works like the contact list on your phone.
You don’t remember people’s phone numbers—you remember their names. DNS does the same thing for websites. Instead of remembering a long number like:
142.250.183.206
You can simply type:
google.com
DNS converts the name into the number behind the scenes.
How the Domain Name System Works (Step-by-Step)
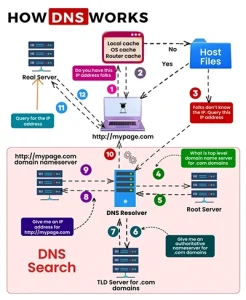
Here’s what happens in milliseconds when you visit a website:
1. You Type a Domain Name
You enter a website address in your browser, such as example.in.
2. Your Browser Checks Local Cache
Your device first checks if it already knows the IP address from a previous visit.
3. Request Goes to a DNS Resolver
If not found, the request is sent to a DNS resolver (usually provided by your hosting company or ISP).
4. Resolver Contacts Root Servers
The resolver asks the root DNS servers where to find information for that domain extension (like .com or .in).
5. TLD Server Responds
The Top-Level Domain (TLD) server directs the resolver to the authoritative nameserver.
6. Authoritative Nameserver Gives the Answer
This server provides the exact IP address of the website.
7. Website Loads
Your browser now connects directly to that server and displays the website.
All of this typically happens in under one second.
Why DNS Is Important for Every Website
DNS is not just a technical detail—it directly affects:
- Website speed
- Reliability
- Email delivery
- Security
- Global accessibility
Without DNS, users would need to memorize numerical IP addresses for every site they visit.
Real Example for Indian Website Owners
Let’s say you register a .in domain for your business. That domain must be connected to your hosting server using DNS records.
At WebHostingPeople, we act as an accredited registrar for .in domains, which means domains are issued directly under official registry standards. For instance, a .in domain is available at ₹555 per year, and DNS configuration is included as part of normal domain management so your website connects correctly.
Common Types of DNS Records (You’ll See These in Your Control Panel)
| Record Type | Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| A Record | Connects domain to an IP address | Point domain to hosting server |
| CNAME | Redirects one name to another | www to root domain |
| MX Record | Handles email routing | Connect domain to email service |
| TXT Record | Verification & security | SPF, DKIM setup |
| NS Record | Defines nameservers | Links domain to DNS provider |
These records are usually managed from your hosting or domain dashboard.
difference between domain and hosting
How DNS Affects Website Speed
A slow DNS lookup can delay your website before it even starts loading. That’s why quality DNS infrastructure matters.
Reliable DNS ensures:
- Faster initial connection
- Reduced downtime risk
- Better global performance
- Improved user experience
This is especially important for Indian businesses serving visitors across different regions.
DNS vs Domain vs Hosting (Quick Comparison)
| Feature | Domain | DNS | Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|
| What it is | Your website name | Translator system | Where files live |
| Visible to users | Yes | No | No |
| Needed to run a site | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Example | yourbusiness.in | Converts to IP | Stores website data |
Think of it like this:
- Domain = Address
- DNS = Google Maps
- Hosting = The Building
People Also Ask
Is DNS the same as a domain name?
No. A domain name is the human-readable address, while DNS is the system that translates it into an IP address.
Can a website work without DNS?
Not practically. Without DNS, users would need to enter IP addresses manually.
Does DNS affect SEO?
Indirectly, yes. Faster DNS resolution improves site speed and availability, which supports better search performance.
Who manages DNS for a website?
Usually your domain registrar or hosting provider manages DNS settings.
ICANN overview of how DNS works
When Do You Need to Configure DNS?
You typically update DNS when:
- Connecting a new domain to hosting
- Migrating to a new server
- Setting up business email
- Adding CDN or security services
- Launching a new website
Most users only interact with DNS occasionally, but it’s critical during setup.
FAQs
How long do DNS changes take to update?
Usually between a few minutes and 24 hours, depending on propagation.
Is DNS difficult to manage for beginners?
No. Most providers offer simple dashboards where records can be added or edited without technical knowledge.
What is DNS propagation?
It’s the time required for updated DNS information to spread across global servers.
Can wrong DNS settings break a website?
Yes. Incorrect records can prevent your domain from connecting to the correct server.
Do I need to change DNS after buying a domain?
Only if your hosting is on a different provider. Otherwise, it may already be configured.
DNS is one of the internet’s foundational systems. It quietly translates domain names into IP addresses so users can access websites without needing to understand the technical structure behind them.
Whether you’re launching a personal blog or a business site, understanding how DNS works helps you make better decisions about domains, hosting, and performance. It’s not something you manage every day—but when you need it, knowing the basics saves time and prevents confusion.
For website owners using services like WebHostingPeople, DNS is already integrated into the domain and hosting environment, making it easier to connect your domain, configure records, and keep your site accessible without dealing with complex infrastructure.